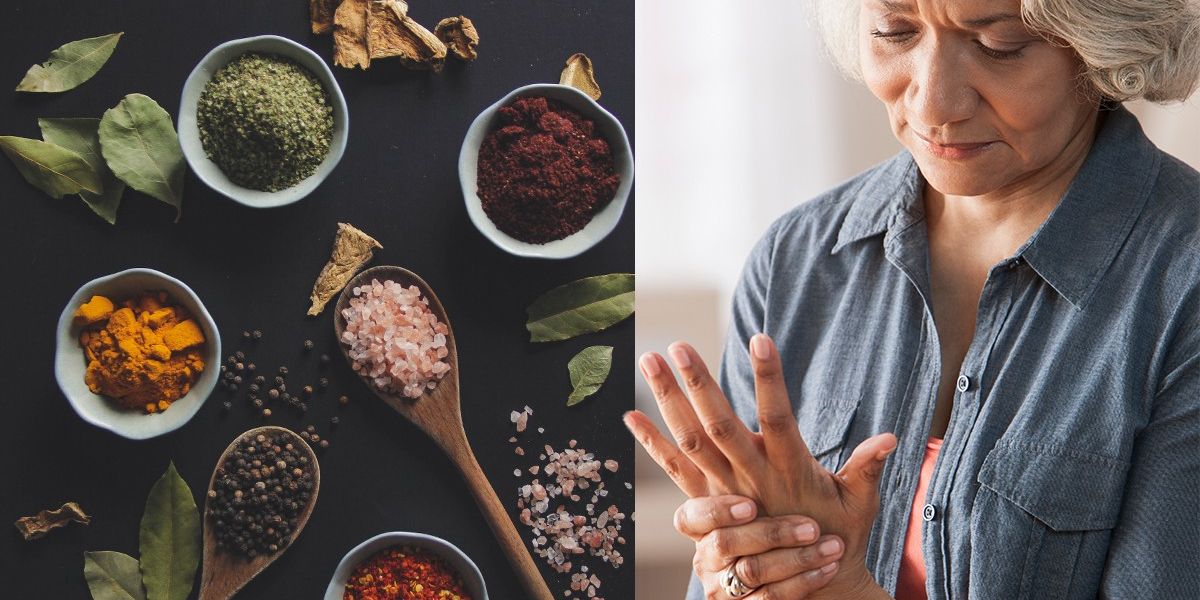


Eating too much salt may trigger rheumatoid arthritis (RA), several studies suggest.
The findings should raise alarm bells in Britain, where the average household exceeds the daily recommended intake of 6g of salt per day.
RA is an autoimmune condition, meaning your immune system attacks healthy body tissue. This misfiring causes severe inflammation of the joints, deforming them and affecting their functionality.
Research has also suggested that a high salt intake may be a risk factor for autoimmune diseases like inflammatory arthritis in people.

Salt stimulates immunological processes that lead to inflammation, research suggests
GETTY
.
Likewise, a study of 18,555 people linked a high sodium intake to an increased risk of RA.
And an animal study found that arthritis was more severe in mice that consumed a high-salt diet than in those whose diet had less salt.
It’s thought that salt (sodium chloride) intake above 6g per day may promote inflammation due to changes in the immune system.
Salt intake may also increase the risk of RA via an indirect route.
Excessive salt intake can also increase the risk of high blood pressure, which has been linked to inflammation in the body.
How to cut down on salt
Often, you can be consuming too much salt without even realising it. That’s the biggest sources of salt in our diet are bread, breakfast cereals, meat products and ready meals – not the salt shaker.
The NHS recommends the following tips to cut back on salt:
Try not to use too many sauces that can be high in salt, such as soy sauce, gravy granules, ketchup, mustard, mayonnaise and brown sauce, the health body adds.
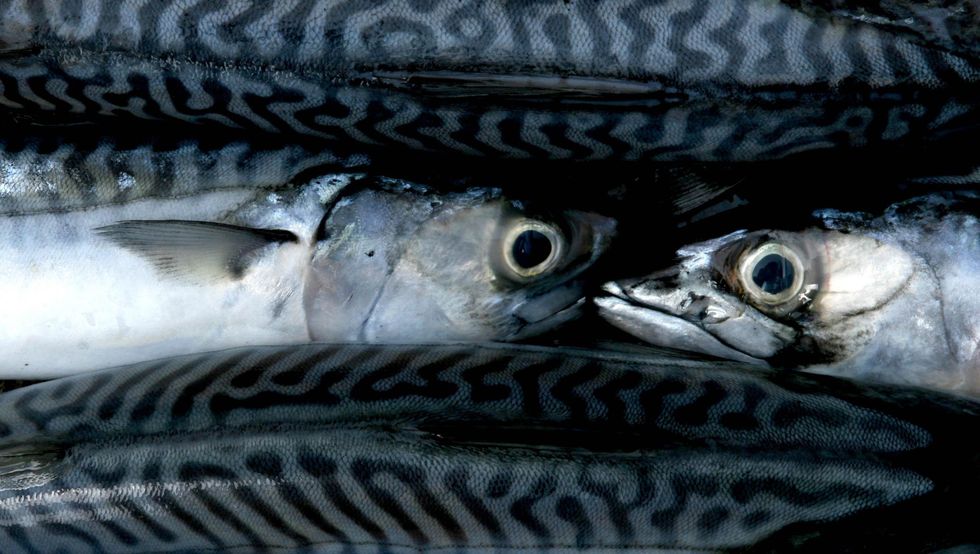

Oily fish
PA
What can help?
One way to calm inflammation is to eat oily fish, such as salmon or mackerel. Oily fish contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are potent inflammation fighters.
Omega-3s interfere with immune cells called leukocytes and enzymes known as cytokines, which are both key players in the body’s inflammatory response.
“The marine omega-3 fatty acids nip inflammation in the bud before it ignites. They really help to tamp down inflammation in the body on a cellular level,” said Kim Larson, a Seattle-based nutritionist and Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Spokesperson.
Research finds that people who regularly eat fish high in omega-3s are less likely to develop RA. And in those who already have the disease, marine omega-3s may help reduce joint swelling and pain.
24World Media does not take any responsibility of the information you see on this page. The content this page contains is from independent third-party content provider. If you have any concerns regarding the content, please free to write us here: contact@24worldmedia.com
Do you believe the Covid vaccine had negative side effects? VOTE HERE

Latest Google layoffs hit the Flutter and Python groups

‘Women’s rights have been attacked constantly!’

Here’s your chance to own a decommissioned US government supercomputer

AWS S3 storage bucket with unlucky name nearly cost developer $1,300

FTC fines Razer for every cent made selling bogus “N95 grade” RGB masks

Apple confirms bug that is keeping some iPhone alarms from sounding
Roundtables: Inside the Next Era of AI and Hardware

Supplements: Ginkgo biloba boosts memory